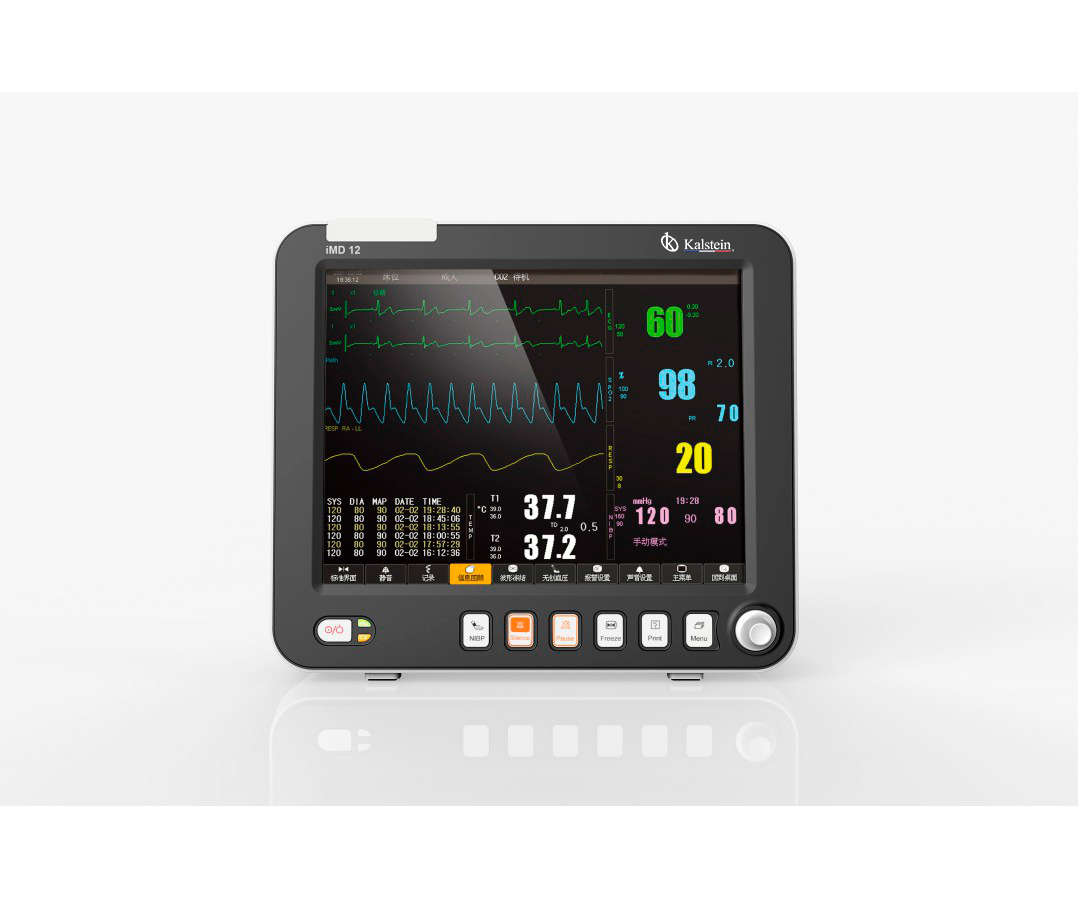
A patient monitor is a medical equipment designed to monitor vital physiological signs of adult and pediatric patients. Through the real-time recording function and the parameters shown, such as ECG, non-invasive blood pressure, body temperature, functional oxygen saturation, among others, it allows a comprehensive analysis of the physiological conditions of the patient. It is intended to use this instrument in hospitals and clinical institutions. Operations should be performed by qualified personnel only.
This equipment has an alarm system that alerts medical personnel when there is an emergency or out of range situation in the patient.
How does a patient monitor work?
This equipment collects, displays and stores all patient vital signs. It works differently for each vital sign. For example, to measure heart rate, the heart’s electrical activity is collected by electrodes and amplified. To measure the breathing rate, the chest’s breathing movements are gathered and amplified. To determine the amount of oxygen the patient does through his pulse.
All these parameters are displayed separately in the Vital Signs Monitor. In the event that any of them are below or above the normal for the patient’s age, or any other adverse activity is generated, an alarm is triggered to alert medical professionals. These alarms are visual and sound, although they can be easily silenced if you are trying to solve the problem that has generated them.
Vital signs monitoring is especially performed in patients undergoing anesthesia, medications or any other treatment that determines the need for blood, medication variation or volume replacement such as a plasma expander.
What are the parameters displayed by a patient monitor?
There are five basic parameters that record and display today’s patient monitors:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Electrodes are placed on the person’s body to record and amplify the heart’s electrical impulses.
- Respiration (RESP): Controls respiratory rate by measuring chest impedance using two electrodes used in the ECG.
- Temperature (TEMP): Using a thermometer, it also shows the temperature the patient has at all times.
- Noninvasive pressure (NIPP): Noninvasive blood pressure (BP) is obtained by using an electronic sphygmomanometer and the bracelet is placed on the person’s arm.
- Oxygen saturation (SpO2): A pulse oximeter is placed on the person’s finger, which gives off light at two different wave densities, to determine the level of oxygen in the blood.
Other parameters that can be registered in more advanced models are:
- Invasive pressure (IP): A sensory catheter inserted into a patient’s artery may increase blood pressure more accurately than noninvasive pressure.
- Venous oxygen saturation (SvO2): A catheter is inserted into the superior vena cava for greater accuracy in determining its level of oxygen in the blood.
- Intracranial pressure (ICP): An intracranial catheter is inserted into the patient to measure pressure within the skull.
In Kalstein We are MANUFACTURERS and we have excellent medical equipment such as patient monitors at the best PRICES in the market. So we invite you to take a look: HERE