What are the benefits of using a Colorimeter in the Biochemistry Laboratory?
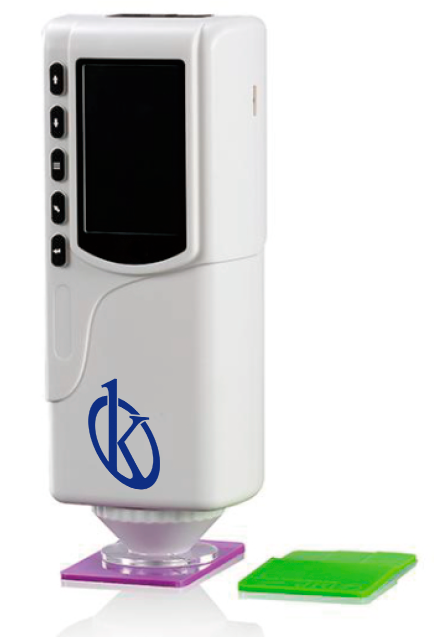

Colorimeters are one of the most essential biochemistry laboratory equipment used in research laboratories. These devices are used to measure the concentration of different solutions and allow scientists to extract reliable and accurate data. Compared to traditional methods of measuring solutions, Colorimeters offer several advantages that make their use necessary for biological studies. Kalstein as a manufacturing company exposes in this article some of the main benefits that Colorimeters offer to Biochemistry laboratories.
What adjustments should be made to obtain the best results with the Colorimeter in the Biochemistry Laboratory?
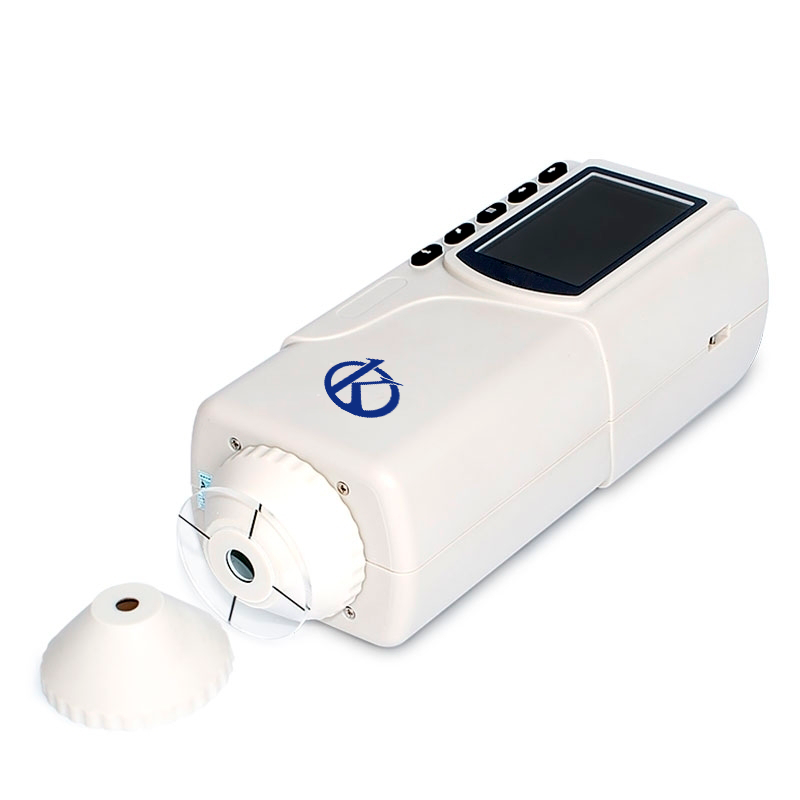
The colorimeter is a widely used device in the biochemistry laboratory, and is one of the main diagnostic instruments in a laboratory. This means that its correct use and the necessary adjustments are essential to obtain the best results. Therefore, below we will discuss the adjustments that need to be made to achieve the best performance of the colorimeter in the biochemistry laboratory.
How does the use of Electrophoresis contribute to the microbiology Laboratory?
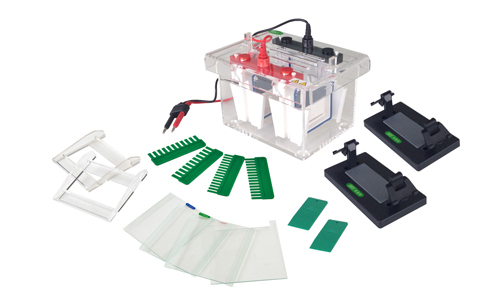
Electrophoresis is an important tool for the separation and analysis of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates. This technique has been widely used in the microbiology laboratory, from the identification of microorganisms and quantification of protein expression to the study of genetic patterns. This form of analysis has greatly assisted microbiologists in obtaining accurate results that might not otherwise be possible.
What are the correct steps to perform an Electrophoresis?
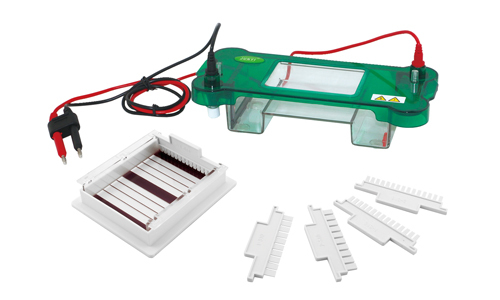
Electrophoresis is a technique used in the laboratory to separate and purify molecules, usually proteins and nucleic acids. It is based on the mobility of ions in a wet medium subjected to an electrical gradient.
Use of thermostatic magnetic stirring Bath in biochemistry Laboratories

The thermostatic magnetic stirring bath is a useful device for temperature control in biochemistry laboratories. This tool has become one of the most essential parts of a biochemistry laboratory inventory, and therefore, it is useful to study its applications in such a setting. This article will discuss the uses and benefits of the thermostatic magnetic stirring bath in biochemistry laboratories.
Medical applications of laboratory Water Baths

In recent years, laboratory water baths have become an indispensable component of modern laboratory equipment. These units have numerous medical applications, and it is important to know their uses and functions to understand the importance of their use. In addition, it is essential to choose the right unit to take full advantage of their benefits.
Development of Biological Laboratory Autoclave Safety and Contingency Plans.
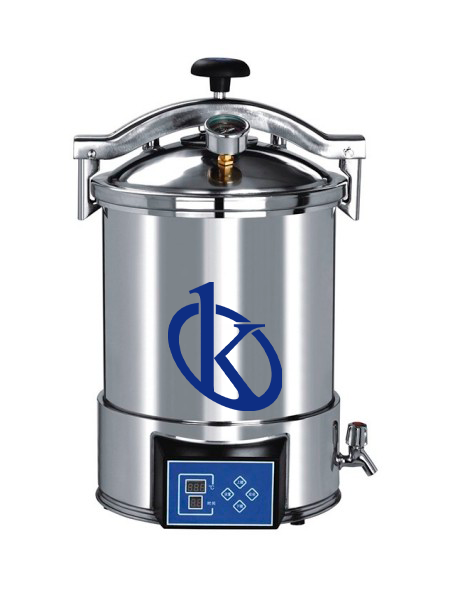

The development of biological laboratory autoclave safety and contingency management plans is an essential tool to ensure the safety and optimal performance of these devices in the scientific work environment. Technology is constantly changing and improving, which means that safety and contingency plans must be regularly reviewed and updated to maintain the most effective safety methods.
Effectiveness of Autoclaves to Prevent Contamination in the Biological Laboratory.
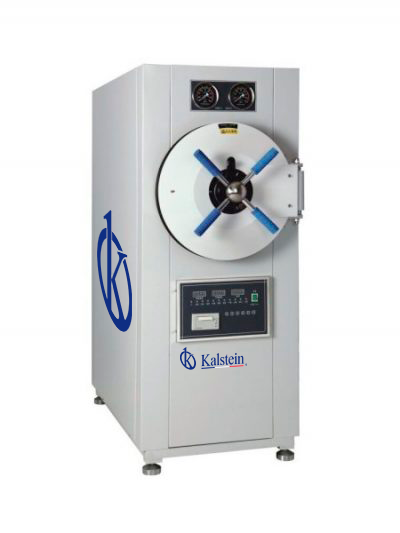

In biology, autoclaves are critical to prevent contamination. These devices provide a safe and efficient way to process waste and other hazardous biological materials. At the same time, they have the ability to protect laboratory personnel from dangerous biological diseases. These features make it essential for the prevention of contamination in the biological laboratory.
Which is an infusion pump in nursing?
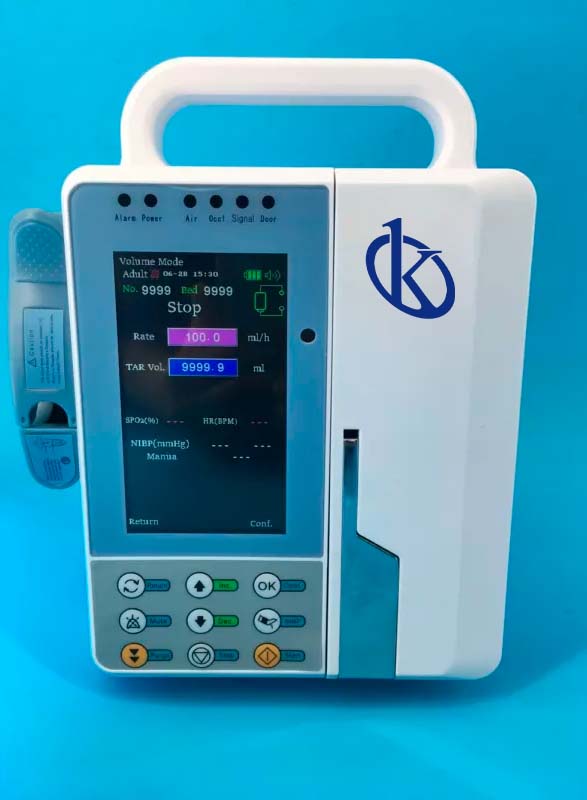
Infusion pumps are artificial energy devices capable of providing a positive influence of liquid to infuse in patients, providing greater accuracy and safety of drugs than traditional methods of flow control (controllers), thus avoiding bacterial agents and in turn decreasing the percentage of human errors.
Differences between an infusion pump and a syringe pump
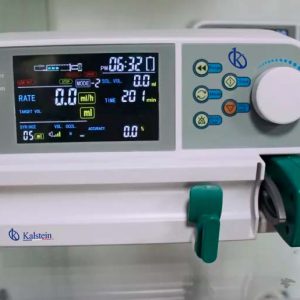
Infusion pumps and syringe pumps are medical equipment that allows drugs or solutions to be delivered to the patient’s body in controlled quantities and accurately. They are used when it is key to give the patient a specific amount of a drug or solution at a certain rate or for a specific amount of time.

