What are the technical characteristics of an analytical balance?
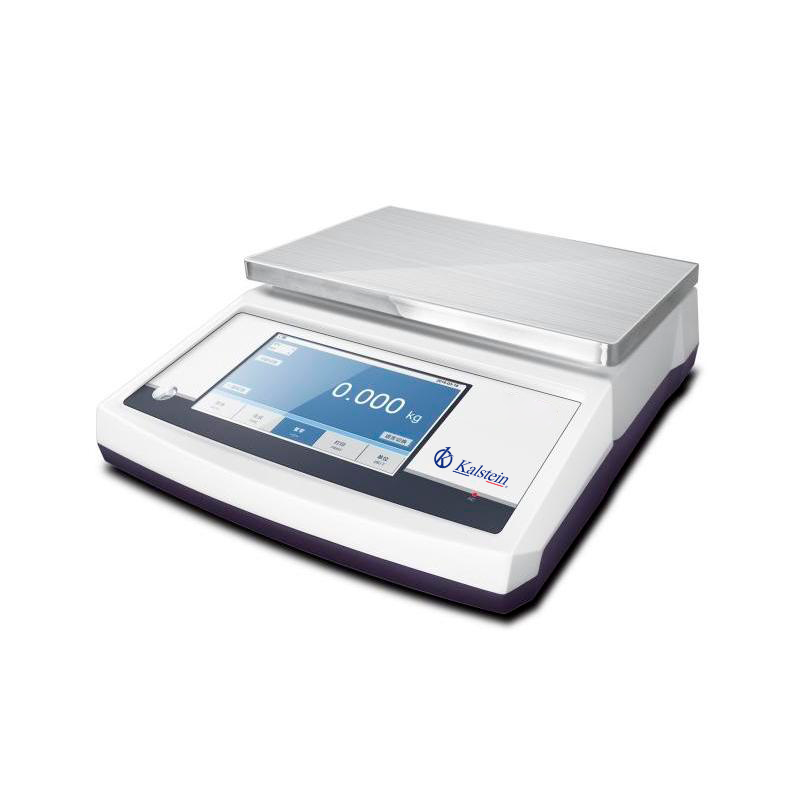

An analytical balance is a laboratory instrument capable of providing fairly accurate measurements, as they are equipped with a system capable of measuring minimal differences in mass. They are usually designed with a transparent box with doors for the door, which isolates the balance from factors that may affect its operation and operation.
Analytical balance: What are the applications and uses?

Analytical balances are a special type of balance that offers very accurate measurements, because they have a system capable of measuring minute differences in mass. They are manufactured within a transparent box with doors to isolate it from certain factors that may affect its operation. Therefore, due to the need for extreme precision in the measurements carried out, they must be in specific rooms for handling, with controlled environmental conditions.
Differences between laboratory balances?
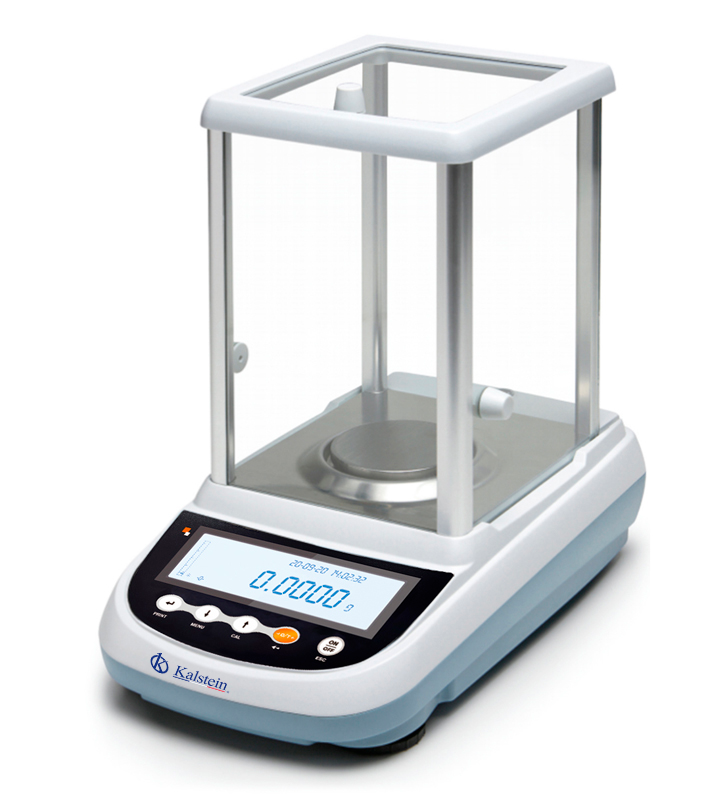

Laboratory scales are devices that allow to determine the weight of a body, that is, they measure the mass of a body under a very small range of uncertainty, therefore, they usually offer very accurate measurements, reason that makes them essential instruments to carry out analytical, chemical and formulation operations in industries, pharmaceutical and quality control laboratories.
Laboratory scales: care and maintenance
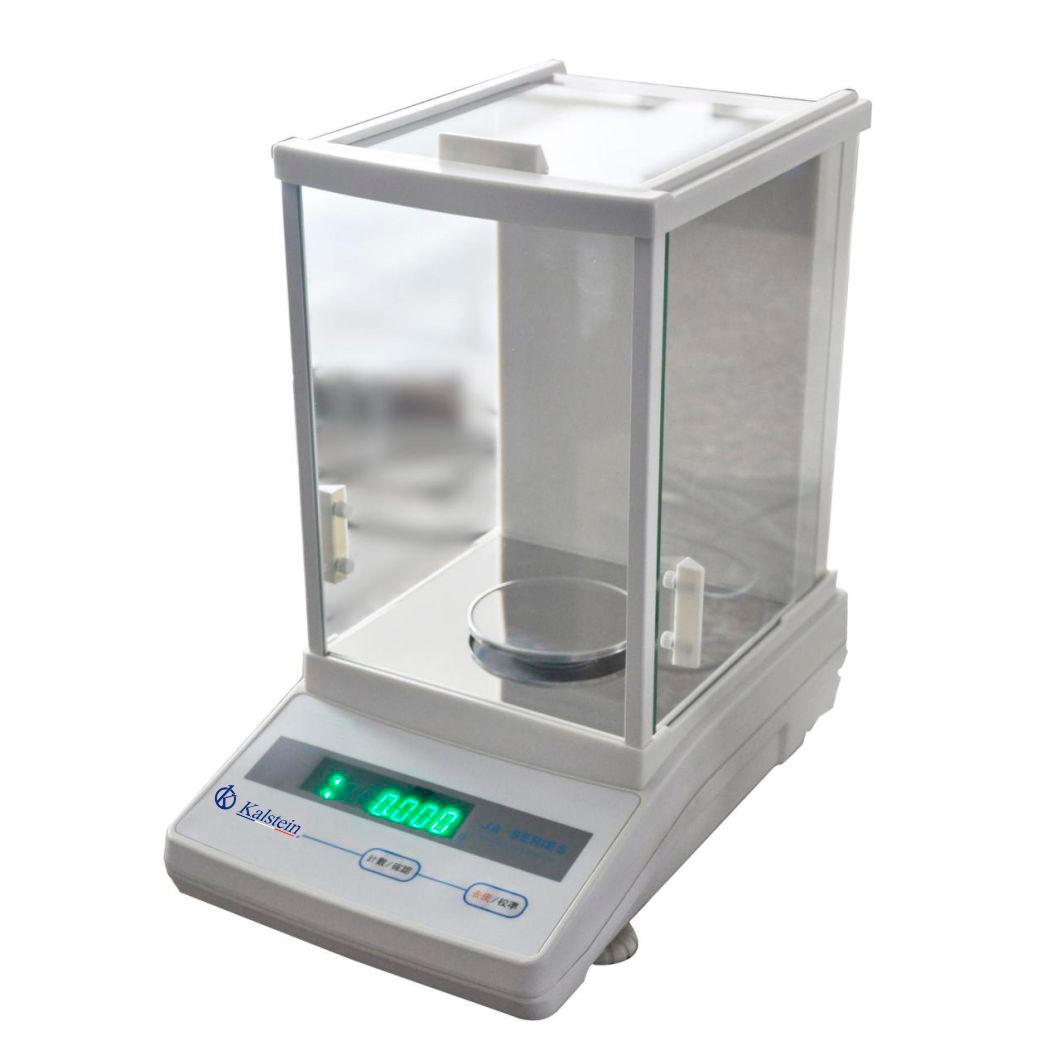

These instruments are characterized by providing accurate weighing, so they are used in industries and clinical laboratories, where highly accurate weighing is required, so they must always be in the most optimal conditions guaranteeing their function; the variety of applications that have the scales requires that the staff perform proper maintenance and care.
What are the types of laboratory balances?
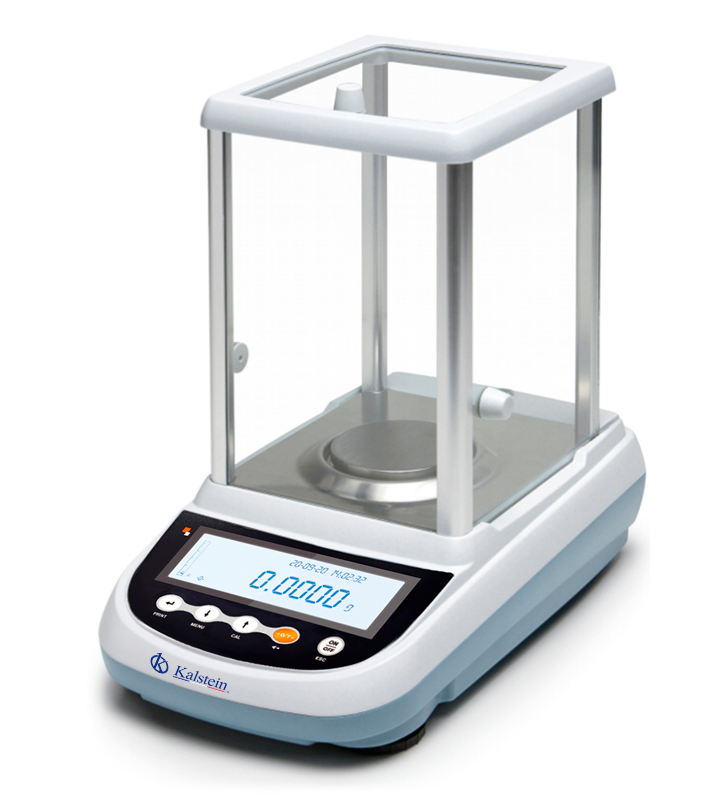

Laboratory balances are instruments that allow determining the weight of a body, that is, they are responsible for measuring the mass of a body under a very small range of uncertainty, therefore, they usually offer very precise measurements as a result, so they are essential equipment in analytical, chemical and formulation operations in industries, pharmaceutical laboratories and quality control.
What is a UV-VIS spectrophotometer?
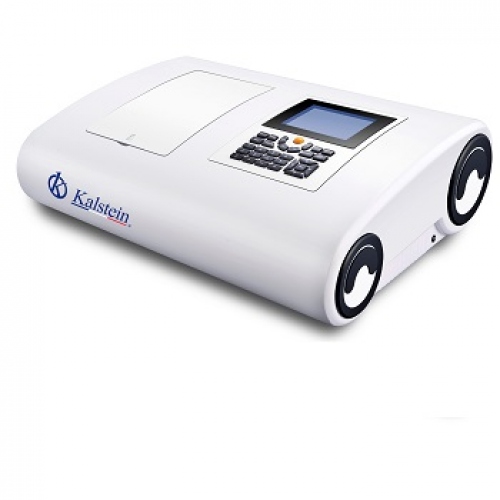

A spectrophotometer is a piece of equipment used to measure the absorbance of a sample, as a function of the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. There are several types of spectrophotometers. These are grouped according to the type of sample analyzed; There are atomic absorption and molecular absorption (commonly known as a UV-VIS spectrophotometer).
Spectrophotometer, types and parts
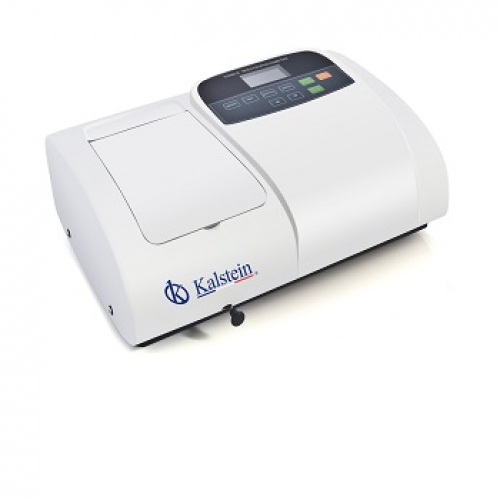

A spectrophotometer is a laboratory instrument used to measure the absorbance of a sample, as a function of the wavelength of an electromagnetic radiation, and thus to know the concentration of the substances in a solution. In other words, it allows to know the concentration of the substances in a solution and thus analyze them from the quantitative point of view.
Importance of a spectrophotometer in a laboratory
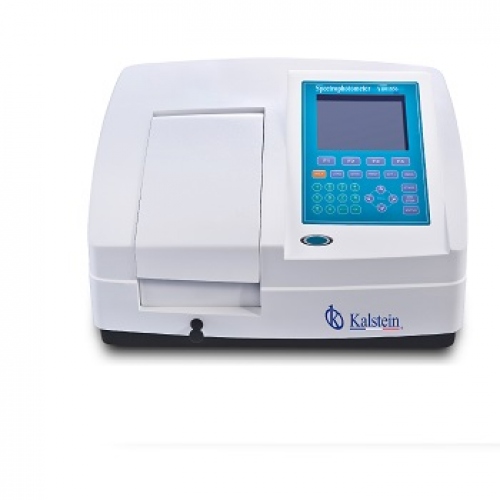

A spectrophotometer is an instrument widely used in laboratories to measure the absorbance of a sample, depending on the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation, and thus know the concentration of substances in a solution.
What is it? and How is it used? a spectrophotometer
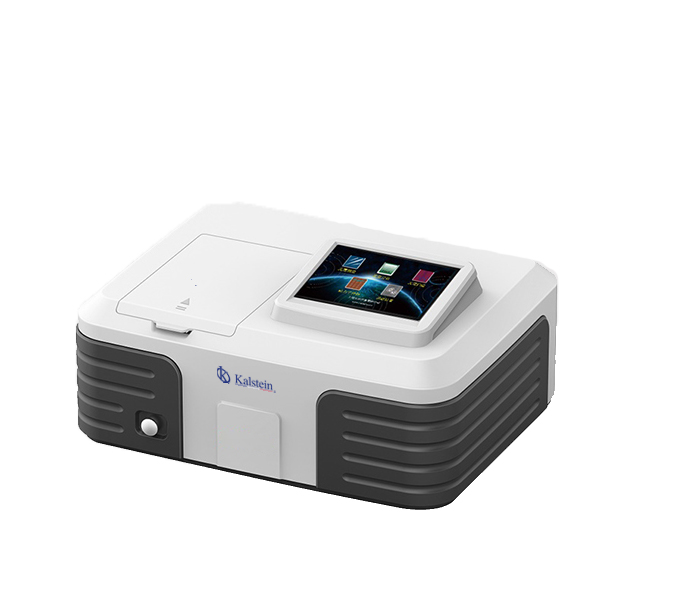
A spectrophotometer is a piece of equipment that measures how much light a substance absorbs. Its efficiency, resolution, sensitivity and spectral range will depend on the design variables and the selection of the optical components that comprise it. Spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the transmission properties of a material based on the light wave.
Power sources: when it is necessary to use it in the laboratory.

They are necessary in laboratories, because they are devices or equipment that are able to convert the alternating current into direct current, being able to regulate it according to the needs of the laboratory area, they are used to distribute or power other equipment so that they work directly from the electrical energy without the need for batteries.

