Parameters measured by a patient monitor
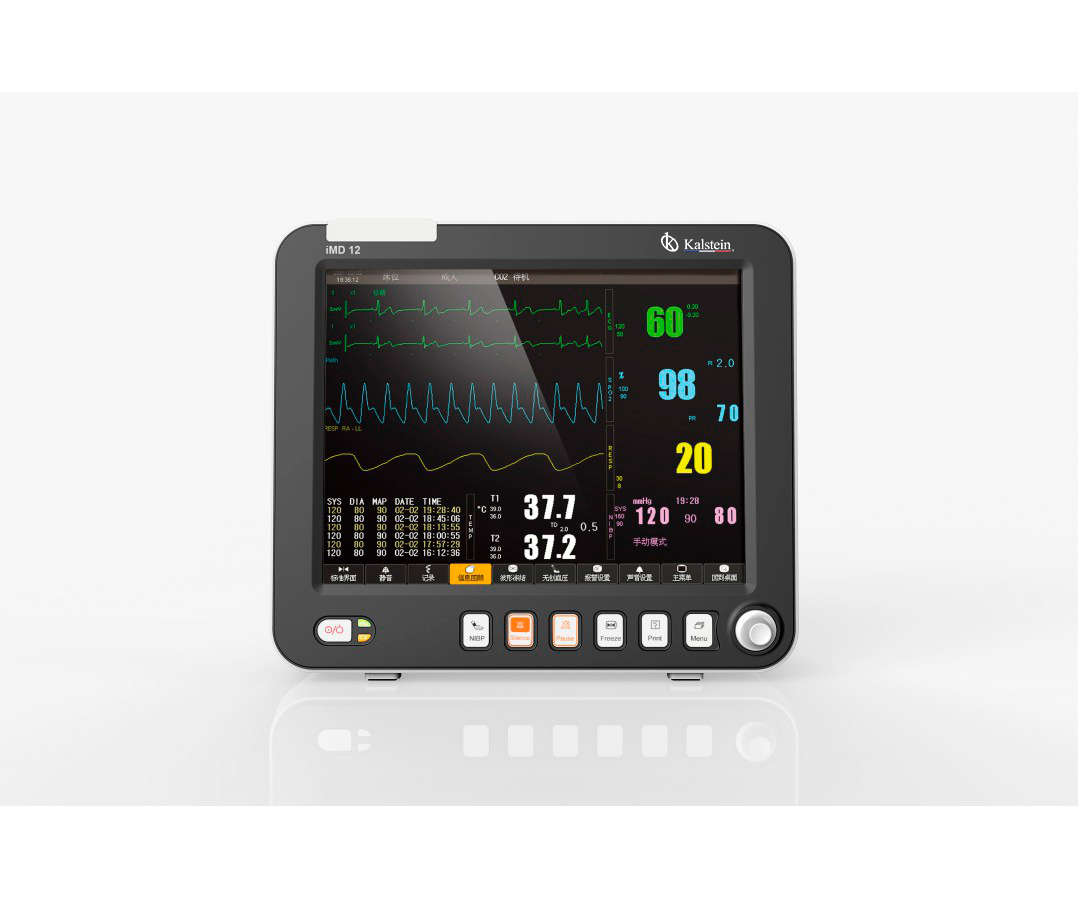
A patient monitor is a medical equipment designed to monitor vital physiological signs of adult and pediatric patients. Through the real-time recording function and the parameters shown, such as ECG, non-invasive blood pressure, body temperature, functional oxygen saturation, among others, it allows a comprehensive analysis of the physiological conditions of the patient. It is intended to use this instrument in hospitals and clinical institutions. Operations should be performed by qualified personnel only.
Monitor pediatric or pediatric patients

A pediatric patient monitor or also called a pediatric monitor is a medical and electronic device that collects, displays, and also stores all vital signs of the pediatric patient. This equipment allows to detect, process and continuously deploy these physiological parameters of the patient such as: breathing rate, blood pressure, body temperature and pulse.
Care and maintenance of an electrocardiograph?
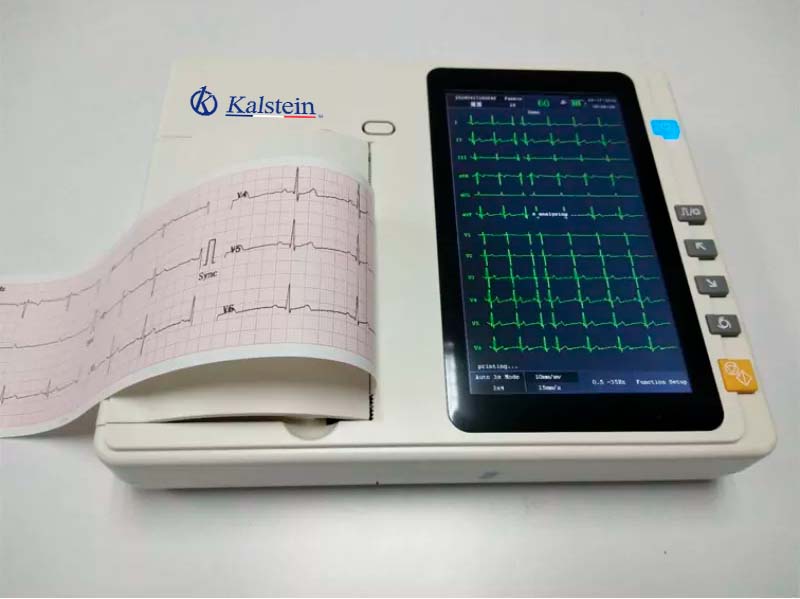
An electrocardiograph is a medical device that analyzes the electrical mechanisms of the heart over a period of time. It works in conjunction with electrodes placed on the patient’s chest and limbs to detect electrical changes.
Pathologies that are detected with an electrocardiograph?
The objective of the electrocardiograph is to search for any pathology in the heart and the effects of treatments and devices on the main organ of the circulatory system, in addition it allows to discover and study diseases such as cardiac arrhythmias, acute episodes of coronary disease and myocardial infarction. It can also be used in preoperative investigations, especially in surgery of medium and high complexity, if there are risk factors such as ischemic heart disease, diabetes, stroke, heart failure or renal dysfunction.
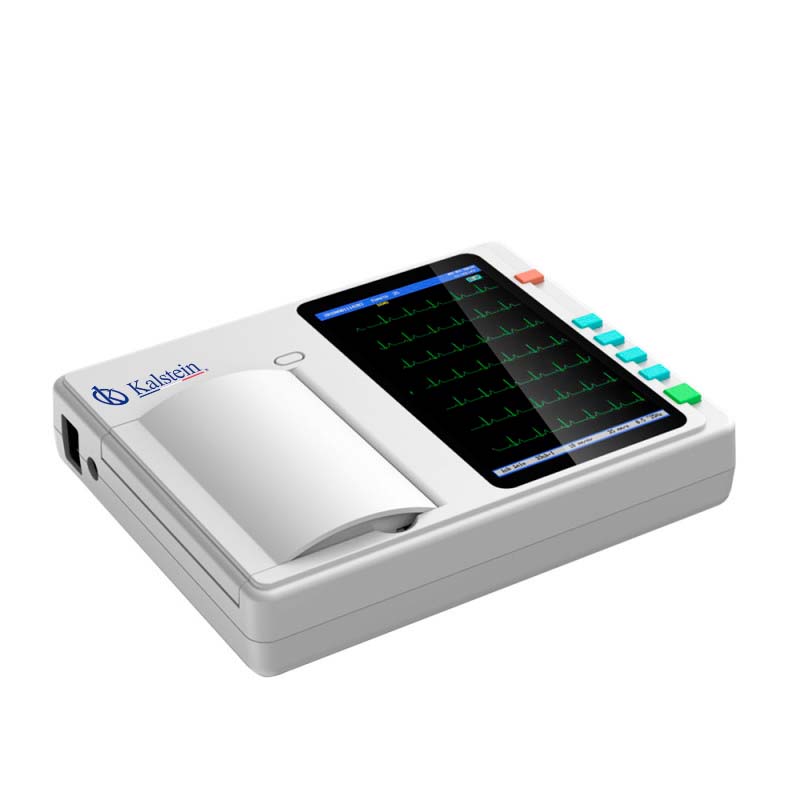
What are the differences between a mono channel and multichannel electrocardiograph?
The electrocardiograph is a medical team in charge of performing tests called electrocardiogram (ECD), and detect the signals of the heart, and in turn, to diagnose some of the diseases of the heart. This device is essential in all health centers, especially in cardiology units.
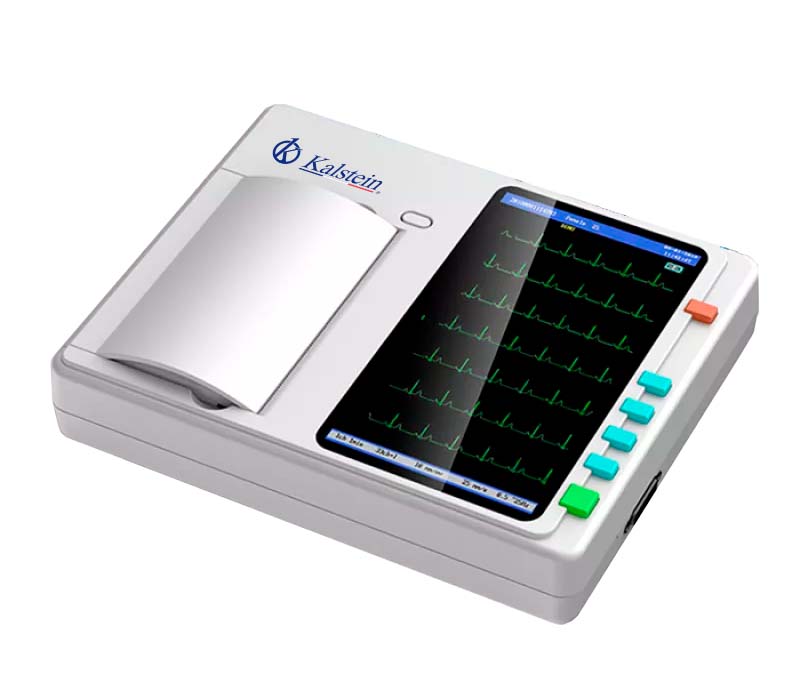
What are the criteria for selecting your ideal electrocardiograph?
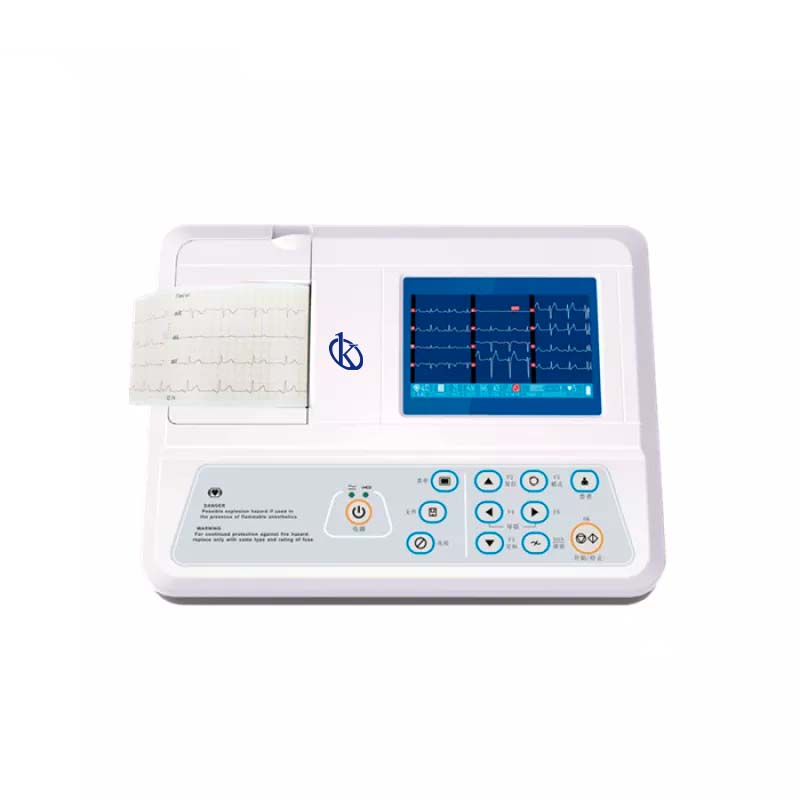
Electrocardiographs are vital medical equipment to provide good health services, so it is an indispensable element in any medical center, whatever its purpose. Generally, its function is to detect heart disease or any type of malfunction or abnormality that presents the heart or its chambers.
Electrocardiographs: How do they work?

At some point you’ve probably wondered how an electrocardiograph works? This medical device is part of a science called bioinstrumentation, a branch of biomedical engineering. It is responsible for recovering specific biosignals from the human body and then processing them in such a way that doctors can interpret them to obtain a diagnosis of the patient in the least invasive way possible.
Electrocardiographs: characteristics, types and models
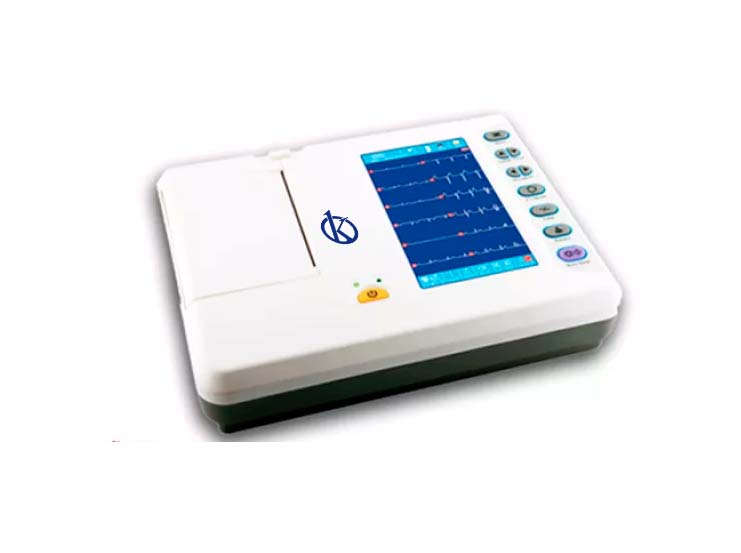
An electrocardiograph is a medical device for clinical diagnosis that captures and expands the electrical activity of the patient’s heart through the use of electrodes. The recording of this activity is called an electrocardiogram (ECG), which is defined as the continuous recording of electrical impulses in the heart.
What are the Microscopic Techniques for Determining Influenza A Virus?

Influenzavirus A is a genus of virus belonging to the family Orthomyxoviridae. It is the virus that causes influenza A disease; influenza A is generally stronger and more virulent than the other minor antigenic variants. Influenza A virus usually causes disease only in birds, but it can infect several mammalian species, including humans. The known subtypes of this virus are endemic to birds, so it is considered a bird disease, yet due to the contagion that has occurred in humans in recent years, especially in countries in Asia, it is a virus that is closely monitored.
The use of the Microscope for the detection of Hepatitis B virus

Hepatitis is a disease characterized by affecting the liver, causing inflammation. It can be acute or chronic type, if the inflammation is recent is said to be acute hepatitis, however, if inflammatory processes last more than six months, then it is spoken of chronic hepatitis. All hepatitis is communicable disease, which means it can be prevented. For example, hepatitis A and E viruses are spread by contaminated food and water, so good hygiene and clean water are the ways to prevent them. On the other hand, hepatitis B and C are transmitted through sexual intercourse or blood contact.

