How many phototherapy sessions are needed?
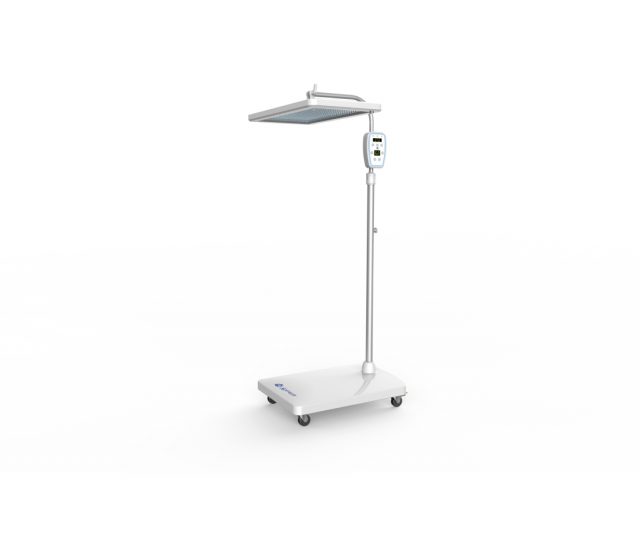

Phototherapy is a technique used in several fields of medicine where the skin is exposed to light sources for a certain time, either to treat skin conditions, due to the use of UV radiation for its anti-inflammatory properties or as the treatment of choice in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia where light is used for its ability to reduce serum bilirubin levels.
What happens after phototherapy?

Phototherapy is a methodology used to treat neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, a clinical condition characterized by high blood bilirubin levels in newborns. Through this technique, these bilirubin values can be reduced by using light.
How is neonatal hyperbilirubinemia treated?
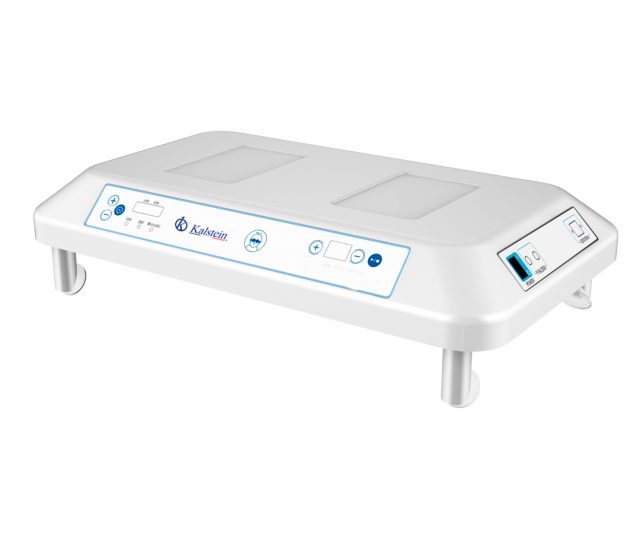

The phototherapy units are medical equipment that expose fluorescent light for the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia in neonates, which are reflected in the color of their eyes, skin and mucous membranes, which causes that yellowish color, because of the elevation of bilirubin in the blood, which has not been processed by the liver, inducing in them an increase in blood levels and as a consequence produces these changes in the neonates.
Laboratory lyophilizer: What are the different types that exist?
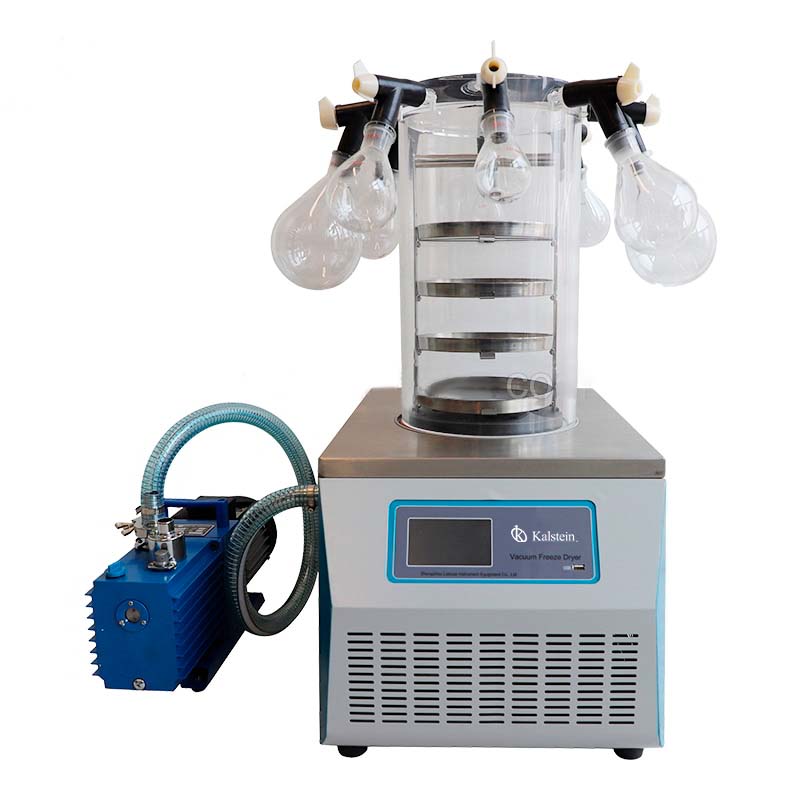

A lyophilizer is a laboratory equipment that allows to carry out lyophilization, that is to say, it is an instrument that is used to remove moisture from a product by cold drying, thus obtaining a dehydrated product that can be rehydrated when needed, thus fully recovering its properties at the time of use.
What is a power source for electrophoresis?

A power source for electrophoresis is a device that manages the current in a constant and direct way to the electrophoresis system, as well as indicates and controls both the supply voltage and the current consumption. In other words, this equipment supplies the energy necessary for this system to function properly; and this delicate laboratory technique can be carried out.
Capillary electrophoresis and gel electrophoresis: What are the differences?

The electrophoresis process is a technique where electrical current is applied to biological molecules, the process consists of separating depending on whether they are large or smaller and has a wide variety of scientific applications, its use focuses on protein research, genetic research, DNA separation and RNA; this technique is widely used in diagnostic tests, and to understand the function of genes and proteins.
What are the principles of electrophoresis?

This technique is widely used in laboratories, especially in those of molecular biology, because it is used in important procedures such as: separation, analysis and purification of RNA, DNA, or proteins, nucleic acids, this process is performed because most biomolecules have an electrical charge where their magnitude depends on the pH of the medium in which they are found; because of this, the biomolecules move when subjected to an electric field to the charge pole opposite to that of the molecule.
How is an ECG interpreted?
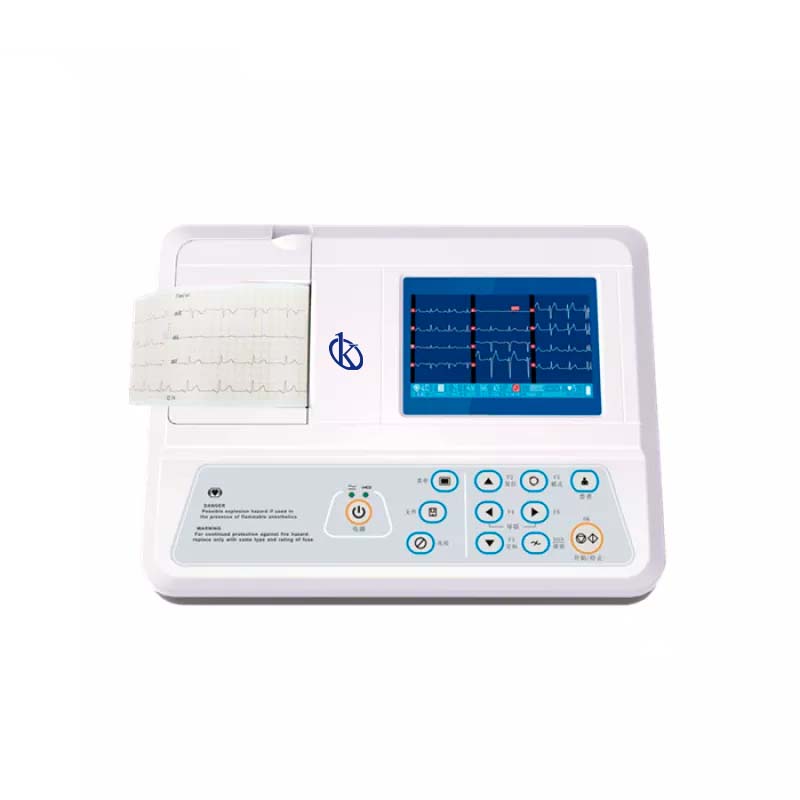
It is called ECG as an electrocardiogram, if it is an evaluation that is done to know the electrical activity of the heart, are performed in the emergency and internal medicine units, consists in the placement of electrodes in different parts of the body, these electrodes send a signal that is recorded in an electrocardiograph, there are ways to perform the examination, one at rest where the patient is relaxed and still, and another where stress test where the patient is kept practicing some physical activity.
What does 12 leads mean in an electrocardiograph?
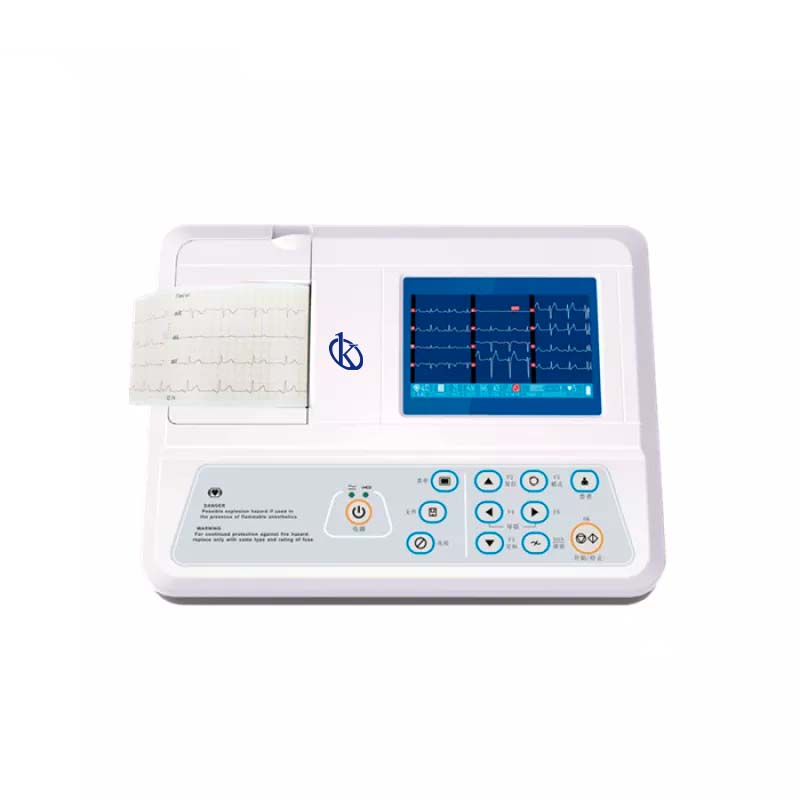
An electrocardiograph of this type is characterized by having 12 channels and recording each of the 12 leads within 2.5 seconds; they allow the visualization of the analysis in real time before printing the records, providing efficiency and improving the accuracy of the patient’s diagnosis; In this way you avoid having to repeat the procedure, a 12-lead electrocardiograph has advantages over other types, such as the ability to send data to the ECG administration system without printing.
What is a multiparameter monitor?
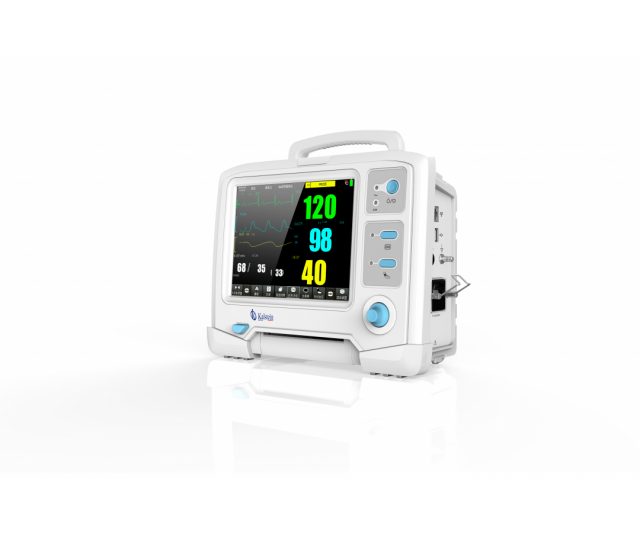
A multi-parameter monitor is an electronic medical equipment that allows monitoring of vital signs of patients in critical condition or who should undergo continuous medical supervision, in case any alteration in the values of these occurs; the vital signs that usually measure and record this device are: heart rate (ECG), respiratory rate (RESP), non-invasive blood pressure (NIP), pulse (PR), oxygen saturation (SpO2), temperature (TEMP), CO2 and invasive blood pressure (PAI).

